Carbon footprint Assessment
BECOME CARBON NEUTRAL
BECOME CARBON NEUTRAL
CARBON REPORTING
FOR BUSINESSES
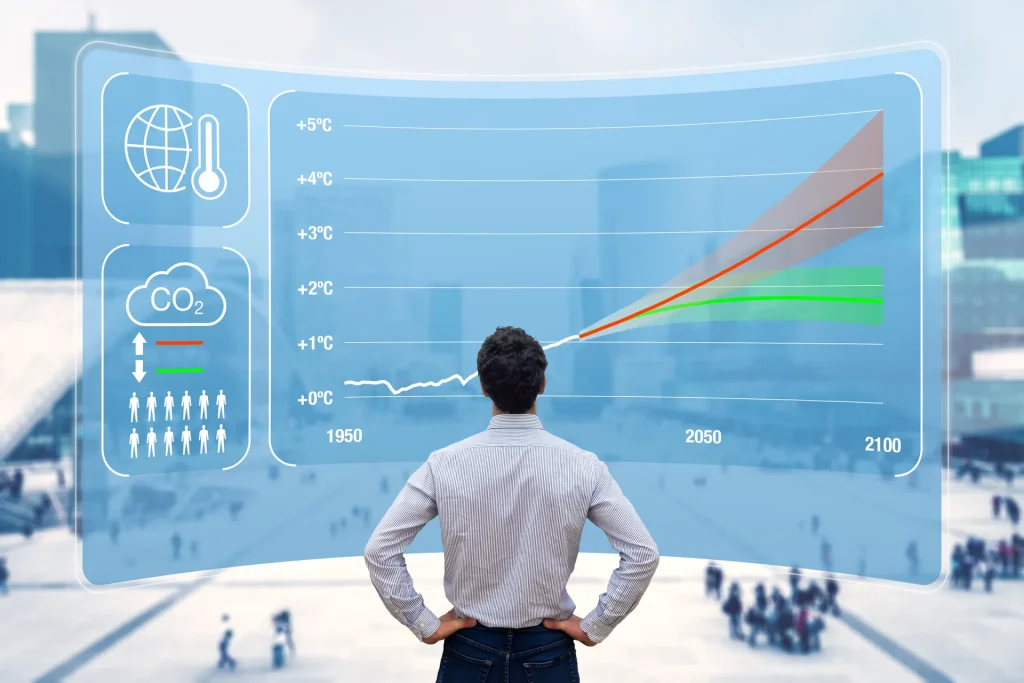
Carbon Smart make carbon accounting easy – report, manage and reduce your carbon footprint. A carbon footprint assessment is a process used to quantify and understand the total greenhouse gas emissions produced directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, product, or activity. It typically involves several steps:
Scope Definition: Determine the scope of the assessment, including whether it will cover direct emissions (Scope 1), indirect emissions from purchased electricity, heat, or steam (Scope 2), and/or other indirect emissions from the value chain (Scope 3).
Data Collection: Gather data on energy use, fuel consumption, transportation, waste generation, and other relevant activities that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. This data can come from utility bills, fuel receipts, travel logs, production records, etc.
Emission Calculation: Use emission factors or other calculation methods to convert the collected data into carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) emissions. Emission factors are typically provided by government agencies, industry associations, or scientific research.
Analysis and Interpretation: Analyze the calculated emissions to understand the sources, trends, and hotspots of greenhouse gas emissions. This can help identify opportunities for emission reductions and prioritize actions to mitigate environmental impact.
Reporting and Communication: Present the findings of the assessment in a clear and transparent manner. This may involve creating reports or presentations that communicate the carbon footprint results, key findings, and recommendations to stakeholders, such as management, employees, customers, investors, and regulatory agencies.
Action and Monitoring: Develop and implement strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions based on the assessment findings. Continuously monitor and track progress over time to assess the effectiveness of mitigation measures and identify areas for further improvement.
Carbon footprint assessments are essential tools for organizations and individuals seeking to understand and manage their environmental impact, comply with regulatory requirements, meet sustainability goals, and contribute to global efforts to mitigate climate change.


SERVICES
SCOPE 1,2,3
Scope 1, 2, and 3 reporting refer to different categories of greenhouse gas emissions, each representing a distinct aspect of an organization’s carbon footprint:
Scope 1 Emissions: These are direct emissions from sources that are owned or controlled by the reporting entity. This typically includes emissions from sources like combustion of fuels in owned or controlled equipment, such as emissions from company vehicles or on-site industrial processes.
Scope 2 Emissions: Scope 2 emissions are indirect emissions associated with the consumption of purchased electricity, steam, heating, or cooling. This includes emissions generated by the production of the electricity or energy purchased by the organization.
Scope 3 Emissions: These are indirect emissions that occur in the organization’s value chain, including both upstream and downstream activities. Scope 3 emissions can include emissions from activities such as business travel, employee commuting, transportation and distribution of products, waste disposal, and even emissions associated with the use of sold products.
Reporting on all three scopes provides a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s environmental impact, allowing for targeted strategies to reduce emissions across the entire value chain.
